Angular Momentum in Case of Rotation about a Fixed Axis
Angular Momentum in Case of Rotation about a Fixed Axis: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Angular Momentum of a Rigid Body in Pure Rotation,Conservation of Angular Momentum in Pure Rotation,Angular Momentum and Angular Velocity, etc.
Important Questions on Angular Momentum in Case of Rotation about a Fixed Axis
A man standing on a turn-table is rotating at a certain angular frequency with his arms outstretched. He suddenly folds his arms. If his moment of inertia with folded arms isof that with outstretched arms, his rotational kinetic energy will
When a body is spinning on its axis in absence of any external torque, then choose the wrong statement
Earth shrinks to times of its initial volume. Time period of Earth rotation is found to be . Find the value of .
Angular momentum of a system of particles changes when
Two identical solid spheres are rolling without slipping with velocity over a rough horizontal surface collides elastically as shown. The final speed of centre of mass of sphere (ii) after sufficient long time will be
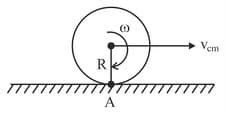
A ring of mass and radius is rolling without slipping, the velocity of point as shown in the figure
A small satellite of mass is revolving round a planet in circular orbit of radius and angular momentum about the centre of the planet. Kinetic energy of the satellite is given by . Find .
A homogeneous rod AB of length and mass is pivoted at the center O in such a way that it can rotate freely in the vertical plane. The rod is initially in the horizontal position. An insect S of the same mass falls vertically with speed on the point C mid-way between O and B. Determine the initial angular velocity in terms of and .
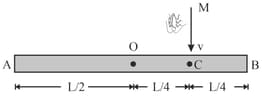
Three uniform rods and each of mass m and length are moving together with velocity on a smooth horizontal surface (direction of is perpendicular to length ) The roads and are hinged at and respectively so that they can rotate freely about and . At an instant during the motion, the middle road is suddenly fixed on the horizontal surface. Find the time taken for the ends and to meet.
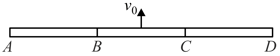
A particle moves in a circular path with constant speed. Find out a point about which the angular momentum of the particle is constant and another point about which it changes with time.
A cat is at rest on a horizontal table mounted on a vertical axis. If the cat begins to walk around the perimeter, what happens to the table ? Explain.
"It is easier to keep your balance on a moving bicycle than on a bicycle at rest ". Why ?
Explain the law of conservation of angular momentum.
Calculate the angular momentum and rotational kinetic energy of the earth about its own axis. Given mass of the earth is and its radius [Moment of inertia of the earth about its axis of rotation is ]
A heavy circular disc is revolving in a horizontal plane about the centre which is fixed. An insect of mass that of the disc walks from the centre along a radius and then flies away. Show that the final angular velocity is times the original angular velocity of the disc.
The mass of a star is and its radius is . It rotates about its axis with an angular speed of . Calculate the speed of the star when it collapses to a radius of ? Assume the moment of inertia of the star to be .
The maximum and minimum distance of a comet from the sun are and . If its velocity nearest to the sun is , what is the velocity in the farthest position? Assume a circular path for the comet.
If earth suddenly contracts by of its present radius by how much would the day be decreased?
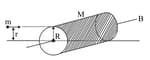
A small body of mass moving with a velocity is strikes a solid cylinder of mass and radius . The cylinder is initially at rest and is mounted on a fixed horizontal axle that passes through the centre of mass. The line of motion of the small body is at a perpendicular distance of from the centre of the cylinder. The small body strikes the cylinder and adheres to its surface. What is the angular speed of the system just after the collision? Assume there is no friction.